Splash Zone Protection Jackets
Corrosion Formation and Process in the Splash Zone on a Pile in the Sea
Definition of Corrosion
Corrosion is the deterioration of metals due to chemical or electrochemical reactions. In marine environments, metal structures are frequently exposed to corrosion, and this process is especially rapid and severe in the splash zone (the area with intense wave and water movement).

Splash Zone
The splash zone is the area just above and below sea level where waves constantly hit the metal surface. This zone experiences continuous wetting and drying cycles, accelerating the corrosion process.
Formation and Process of Corrosion
- Contact with Water and Oxygen: In the splash zone, the metal structure is in constant contact with water and oxygen. These two components are essential for the initiation of corrosion.
- Formation of Electrochemical Cells: Potential differences arise between different regions on the metal surface, leading to the formation of anode and cathode regions. At the anode regions, the metal oxidizes and dissolves as ions.
- Effect of Salt Water: Due to its high salt content, seawater acts as an electrolyte. Saltwater accelerates electrochemical reactions, causing the metal to corrode more rapidly.
- Dissolved Oxygen and pH Changes: The constant movement in the splash zone ensures a high level of dissolved oxygen in the water, which increases the corrosion rate. Additionally, the pH of seawater affects the formation of corrosion products.
- Corrosion Products and Surface Deterioration: Corrosion products (e.g., rust) form on the metal surface. These products can accumulate and facilitate continued corrosion. Over time, the structural integrity of the metal structure deteriorates.

Conclusion
Corrosion in the splash zone can significantly shorten the lifespan of metal structures. Therefore, corrosion control and protective measures are crucial in these areas. Cathodic protection, paints and coatings, and HDPE (high-density polyethylene) protective jackets in the splash zone are common methods used to reduce the rate of corrosion. These methods enhance the durability of metal structures, ensuring long-lasting and safe use.

Splash Zone Protection Jackets
Benefits of Splash Zone Protection Jackets
- Long-Lasting Protection: Provides durable corrosion protection in challenging areas like the splash zone.
- Low Maintenance: Requires minimal maintenance, reducing operational costs.
- Environmentally Friendly: Reduces the risk of chemical pollution, posing no harm to the environment.
- Easy Application: Offers quick and effective installation, lowering labor costs.
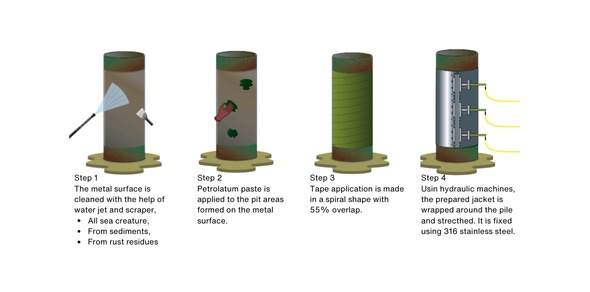
Application of Splash Zone Protection Jacket
Application Areas
-
Outer Layer (HDPE Coating)
- High Durability: High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) coating provides superior protection against physical impacts, chemicals, and UV rays.
- Flexibility: Adapts to the movement of piles, maintaining structural integrity.
-
Inner Layer (Petrolatum Paste and Tape)
- Corrosion Barrier: Petrolatum paste and tape create an effective barrier against corrosion when applied directly to metal surfaces.
- Adhesion and Seal: High adhesion strength prevents moisture and oxygen from reaching the metal surface.
-
Mechanical Connections (316 Stainless Steel Fasteners)
- Corrosion Resistance: 316 stainless steel offers excellent corrosion resistance in seawater and harsh environmental conditions.
- Reliable Connections: Provides strong and dependable connections, ensuring the longevity of the system.
